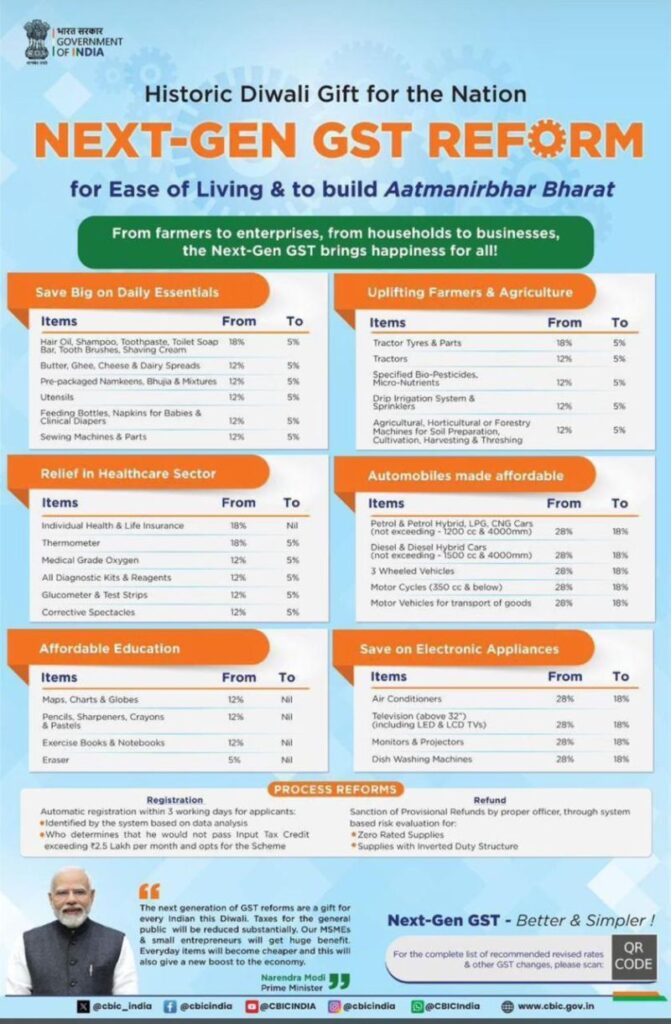
India’s Next-Gen GST Reform marks a significant milestone in the country’s economic journey. Introduced at a time when global trade faces rising tariffs and economic volatility, this reform aims to simplify the Goods and Services Tax (GST) structure across a wide range of sectors from daily essentials and healthcare to education, agriculture, infrastructure, and renewable energy. By reducing GST rates, the government seeks to ease financial burdens on households, strengthen businesses, and stimulate consumption-led growth.
India’s Next-Gen GST Reform brings immediate relief to households by lowering taxes on essentials such as personal care products and dairy. This reduces everyday expenses, eases financial pressure, and encourages higher consumption, which in turn drives demand across industries.
Farmers and the agricultural sector are set to benefit as well. Reduced GST on farming equipment, bio-pesticides, and dairy products lowers input costs, supports sustainable practices, and enhances efficiency in the supply chain, strengthening resilience and overall economic stability.
For Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), the reform simplifies compliance and reduces taxes on critical business inputs. These changes help small businesses operate more efficiently, expand their reach, and improve profitability, fostering competitiveness and formalization.
The renewable energy sector receives a meaningful boost from lower GST on solar panels, making clean energy installations more affordable and supporting domestic manufacturing. While relief for battery backup systems is still awaited, the reduced tax on panels encourages green investment and moves India closer to its sustainable energy goals.
Healthcare and education also gain from the reform. Lower GST on medical devices, medicines, vaccines, and learning resources makes them more accessible and affordable. Additionally, reduced taxes on construction materials support infrastructure projects, create jobs, and stimulate broader economic activity. Effective implementation and monitoring will be crucial to ensure these benefits reach all intended sectors and consumers.
Despite these advantages, challenges remain. Effective implementation is critical to ensure tax reductions reach end consumers and that compliance remains manageable for small businesses. Vulnerable sectors and regions may still face gaps, and areas like renewable energy storage may require further policy attention. Monitoring and adaptive measures will be essential to maximize the reform’s impact.